Composition
- Each Film Coated Tablet Contains:
- Atenolol IP
50 mg
Packing
- 10x10
(Blister)
MRP
- 24.45
Overview
This medicine is called a beta-blocker. It acts on the heart and decreases blood pressure. The medicine can help to reduce your blood pressure or treat your chest pain (angina). It may also help to keep your heart beating regularly if you have palpitations or to protect it after a heart attack.
What is ATMONIL and what it is used for?
The active ingredient of ATMONIL is Atenolol. Atenolol belong to a group of medicines known as beta-blockers; selective Β1 receptor antagonist, which are used to treat a variety of heart and blood vessel conditions.ATMONIL is recommended for the management of hypertension, angina pectoris, cardiac dysrhythmia, and for early intervention in the acute phase of myocardial infarction.
Warnings
Sudden withdrawal of beta-adrnoceptor blocking agent in patients with ischaemic heart disease may result in the appearance of anginal attacks of increased frequency or severity or deteriorate in cardiac state. Discontinuation of therapy should be gradual.
Anaesthesia: Care should be taken when using anaesthetic agents with Atenolol. The anaesthetist should be informed to enable the necessary precautions to be taken.
Atenolol should only be used with caution in patients with controlled congestive cardiac failure or with a family history of asthma. Evidence of developing of either conditions should regarded as signal of discontinue therapy
Contraindications
Atenolol is contra-indicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to Atenolol, second degree or third degree heart block shock.
It should not be given to patients with severe bradycardia.
Uncomplicated or digitalis/ diuretic-refractory heart failure.
Atenolol should not be used in patients with cardiogenic shock..
Side Effects
Nausea (feeling sick)
skin rash with itching or raised lumps on your skin
Vomiting
Diarrhoea
Constipation
Tiredness
low blood pressure (signs include light-headedness, fainting)
shortness of breath
Dosage
This is Preferred Dosage:
Adults:
Hypertension: Usually 50mg daily.
Angina: Usually 100mg daily or 50mg twice daily.
Dysrhythmias: Following control with intravenous atenolol, a suitable oral maintenance dosage is 50-100mg daily, given as a single dose.
Myocardial Infarction: Following treatment with intravenous atenolol, oral atenolol 50mg may be given approximately 15 minutes later, provided no untoward effects occur from the intravenous dose. This should be followed by a further 50mg orally 12 hours after the intravenous dose and subsequent dosage maintained, after a further 12 hours, with 100mg daily. If bradycardia and/or hypotension requiring treatment, or any other untoward effects occur, atenolol should be discontinued.
Renal impairment: The dose may need to be reduced.
Hepatic dysfunction: The dose may need to be reduced.
Elderly Patients:
Dosage requirements may be reduced, especially in patients with impaired renal function.
Children under 12 years of age:
There are inadequate clinical data available on the use of Atenolol in children and for this reason it is not recommended.
Disclaimer:To be taken only after consulting with the doctor.
Storage
Store in the original container .
Special precautions for storage:Do not store above 25oC
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Atenolol competes with sympathomimetic neurotransmitters such as catecholamines for binding at beta (1)-adrenergic receptors in the heart and vascular smooth muscle, inhibiting sympathetic stimulation. This results in a reduction in resting heart rate, cardiac output, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and reflex orthostatic hypotension. Higher doses of atenolol also competitively block beta (2)-adrenergic responses in the bronchial and vascular smooth muscles.Beta blocker
↓
• Decrease vasodilation
• Decrease aldosterone secretion
• Decrease catecholamine release
• Inhibit renin release
↓
Decrease B.P
Pharmacodynamics
Atenolol is a beta-adrenoceptor blocking agent for use in the management of hypertension and angina pectoris. It is a cardioselective beta-blocker selective for cardiac beta1 receptors and has no partial agonist or membrane stabilising activity. The mode of action of atenolol and other beta-blockers in the moderation of hypertension is still not fully understood although its effects on plasma renin and cardiac output are probably of primary importance. Atenolol reduces cardiac output, alters baroreceptor reflex sensitivity and blocks peripheral adrenoceptors. Atenolol has been found to reduce systolic and diastolic blood pressures by about 15% in patients with mild to moderate hypertension. Its beta-adrenoceptor antagonist properties reduce cardiac work. This property improves exercise tolerance in anginal patients.Pharmacokinetics
Atenolol is not completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, its oral bioavailability being of the order 50-60%. It is approximately 5% bound to plasma proteins. The plasma half-life of atenolol is about 6 hours. However, the duration of therapeutic effect is much longer than this, allowing once daily dosing. Atenolol is excreted largely unchanged in the urine and its dosage should be adjusted in renal failure.Interactions
- Beta blocker should only be used with great caution in patients who are receiving concomitant myocardial depressants such as chloroform, lignocaine, procainamide, beta- adrenoceptor stimulants such as isoprenaline, or verapamil or alpha-adrenoceptor stimulants such as noradrenaline, adrenaline (which reverse the hypotensive effects and increase the vasoconstrictor activities).
- Neuron blocking agents such as guanethidine, reserpine, diuretics and other antihypertensive agents, including the vasodilator groups, will have an additive effect on the hypotensive action of the drug.
- Caution should be exercised when transferring patients from clonidine to beta-adrenoceptor blocking drugs. If the beta blocker and clonidine are given concurrently, the clonidine should not be discontinued until several days after withdrawal of the beta-blocker.
- The beta-blocker, atenolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia of anti-diabetic drugs (Acetohexamide, Chlorpropamide, Gliclazide, Glipizide).
- Atenolol crosses the placenta. The safety of atenolol if given in early pregnancy has not been established and its use should therefore be avoided. Beta-blockers reduce placental perfusion, which may result in intrauterine foetal death, immature and premature deliveries. In addition, adverse effects (especially hypoglycaemia and bradycardia) may occur in foetus and neonate in the postnatal period.
- Administration of atenolol in pregnancy may be associated with reduced foetal growth, which is greatest when started in early pregnancy, such as in the second trimester and is related to the duration of treatment. The risk of adverse effects to the foetus or neonate is greater in severely hypertensive pregnancies.
- However, atenolol has been used effectively under close supervision for the treatment of hypertension in the third trimester.
- Atenolol is excreted in breast milk. Breast-feeding can be undertaken but infants should be monitored for bradycardia, respiratory depression, hypotension and hypoglycaemia.
For Patients
Patient InformationWhat should I know before taking medicine? Before you take Atenolol Tablets Do not take these tablets if:
- you are allergic to atenolol or to any of the other ingredients of this medicine
- you have low blood pressure
- you have very poor circulation
- you have phaeochromocytoma (high blood pressure caused by a tumour, usually near the kidney) which is not being treated
- you suffer from metabolic acidosis (abnormal levels of acid in your blood)
- you have another heart problem such as heart block or uncontrolled heart failure
- you have a slow or uneven heartbeat
- Before you start taking the tablets, read the manufacturer's printed information leaflet from inside the pack. The manufacturer's leaflet will give you more information about Atenolol and a full list of the side-effects which you may experience from taking it.
- Always take Atenolol Tablets as your doctor has told you.
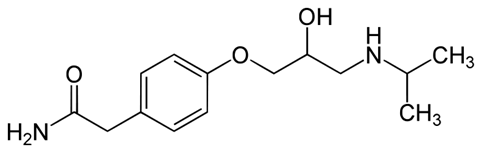
Chemistry
Atenolol is a selective Β1 receptor antagonist, a drug belonging to the group of beta blockers, a class of drugs used primarily in cardiovascular diseases. Atenolol is used for a number of conditions including: hypertension, angina, long QT syndrome, acute myocardial infarction, supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia, and the symptoms of alcohol withdrawal.Structure
Clinical Data
Pregnancy Category | AU: C US: D |
Legal status | Rx Prescription only |
Routes | Oral or IV |
Formula | C14H22N2O3 |
Molecular Mass | 266.336 g/mol |